- Home
- Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic Brain Injury
Head trauma causing traumatic brain injury can happen after many different types of accidents or assaults. These include:
- Falls - The leading cause of all head trauma, home or elsewhere.
- Auto, bike & motorcycle accidents. - A helmet is no guarantee of safety.
- Impact baseballs, soccer and golf balls.
- Sports including football and boxing.
- Assaults with fists, baseball bats and other types of weapons.
- Gunshots.
Many of these traumatic brain injury events will require ICU care.
Direct Brain Trauma
A severe blow to the head with or without a helmet can directly injure the brain. The victim can be unconscious momentarily or for a long time.
At the time of injury, the brain can suddenly be pushed to the other side of the skull and suffer a second injury when the opposite side of the brain hits against the skull.
A brain scan will show any swelling of the injured area or areas. The swelling increases brain pressure with potentially severe consequences.
After severe traumatic brain injury, treatment is directed at keeping the brain pressures under control.
Treatment for brain pressure control includes:
- Ventilator and breathing tube
- Blood pressure control - Kept it in a normal range
- Pressure device in the brain to measure & control brain pressure
- Sedation and other medications to control the brain pressure
- Partially sitting up in bed helps control the pressures in the brain
- Operation to reduce pressure by opening a portion of the skull
Recovery after brain trauma varies with the severity of the injury It can be days, weeks or months.
A slow recovery and inability to come off the ventilator means a tracheostomy and feeding tube will be needed
Questions to Ask
- Who is the doctor in charge? When do the doctors come around?
- Are there other injuries?
- Will my loved one recover? Will they be the same as before the injury?
- Why is he or she not waking up? What happens if they don't wake up?
- Will rehab be necessary?
- What else should we know
- Always feel free to contact me with questions
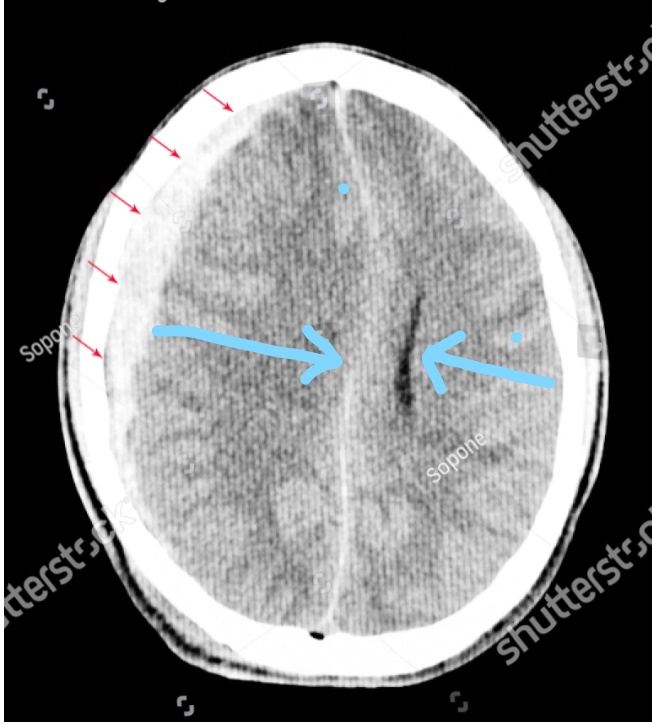
This is a brain scan. The red arrows show where blood(the dull white image which looks like a lens) is pushing the brain away. The bright white all the way around is the skull.
The blue arrow on the left shows how the pressure on the brain from the blood compresses the brain ventricle; the black structure indicated by the right blue arrow.
Traumatic Brain Injury Causing Brain Bleeding
Traumatic brain injury can cause serious bleeding in the brain. This can be life threatening.
The blood can collect be between the brain and the skull or within the brain tissue itself. You may hear one of the following:
- Epidural hematoma
- Subdural hematoma
- Subarachnoid bleed
- Intraparenchymal hematoma
Don't worry about these technical terms; but you will hear them used.
They all mean bleeding occurred and blood is starting to or has clotted.
Patients do not bleed to death from bleeding in the brain.
The problems develop when the blood increases pressure on the brain. You will hear this referred to as ICP - Intracranial Pressure
To reduce the pressure on the brain the doctors will:
- Insert a breathing tube and place the patient on a ventilator.
- Place a pressure monitor on the brain.
- Give sedatives and other medications to control brain pressure.
- If these alone fail, surgery may be needed to remove the blood clot.
- If the brain is badly swollen at surgery, part of the skull will be removed to help reduce pressure.
- The part of the skull removed will be saved and back in the patient at a later date.
Questions to Ask
- If surgery is necessary, when is it and what will they do?
- What are the chances for survival?
- How much recovery can our loved one make?
- How will we know there is no chance of recovery or survival?
- If part of the skull is removed, what happens to it?
- Always feel free to contact me.
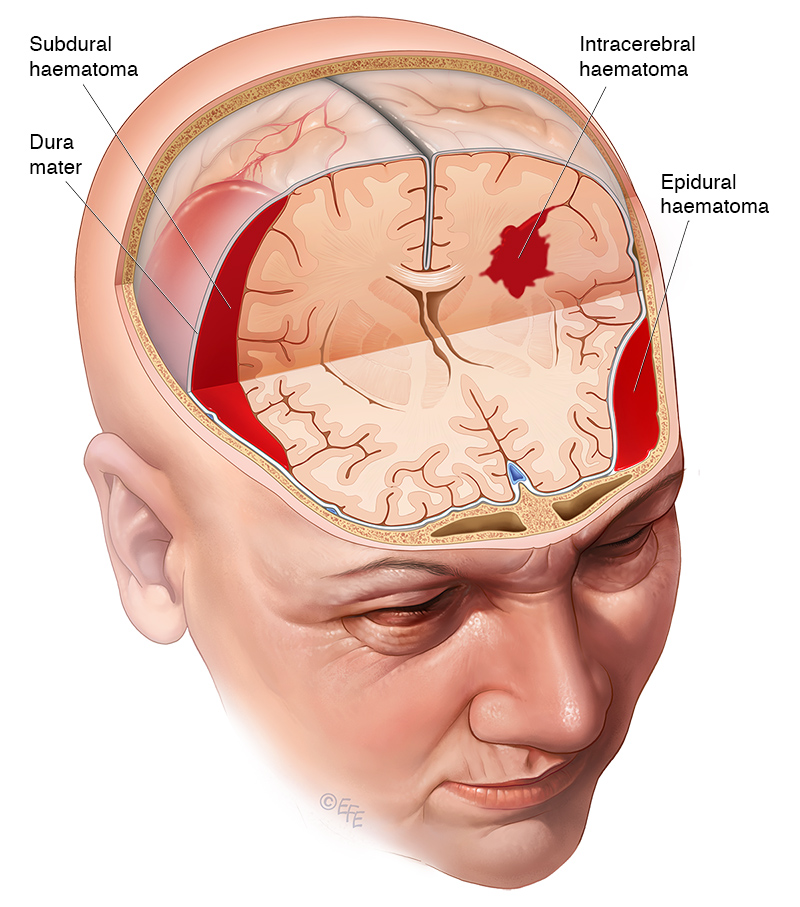
Three types of brain bleeds after head trauma The epidural hematoma is outside the brain whose edge is shown by the white line.
The subdural hematoma is directly on the brain surface.
Intracerebral hematoma is a blood clot in the middle of the injured portion of the brain.
Gunshot Wounds
Gunshot wounds usually require a slightly different approach. The bullet causes widespread damage in the brain.
If considered survivable, immediate surgery will be necessary.
Dead or irreversible damaged brain as well as blood clots need to be removed.
The gunshot also carries debris and bone particles into the brain. These require removal.
At surgery, monitors are placed on or in the brain to measure brain or intracranial pressure(ICP). Catheters to drain out excess fluid might also be placed.
After surgery your family member will require sedation. A ventilator may also be necessary for several days.
Any loss of function will be dependent on the areas of severely damaged or removed brain. It may take 6 months or longer to know the total extent of permanent injury.
What Should We the Family be Doing
Recovery from traumatic brain injury can be very slow.
Patience is difficult; but is really necessary.
Other complications can develop such as infections in the lung or urinary tract. Blood clots in the legs can also occur.
When you visit, talk to your loved one. Even if they don't respond they can often recognize your voice.
If they become agitated when you visit, the nurse may advise some changes in visiting procedures.
If your loved one likes music; bring what they like. Ear buds work better since head dressings can get in the way.
Get updates only from the doctor in charge( ICU doctor, Neurosurgeon or both).
The bedside nurse also knows what is going on.
Recovery is not a continuous uphill course. Temporary setbacks are common.
Some days he or she may seem very responsive. The next day or even later that day they may not do anything.
Do not overly be concerned. These kinds of changes are common after brain injury, and part of the recovery process.
Outcome after Traumatic Brain Injury.
Immediately after brain trauma, survival or recovery can be hard to predict.
It may take 6 months or more to know how much recovery your loved one will obtain.
Depending how awake a patient , a tracheostomy tube may need to stay in place long term to help keep the lungs clear of secretions.
Most recovering severe traumatic brain injury patients will need time in rehabilitation. Most facilities require your loved one to be awake enough to participate in several hours a day of therapy
Those who cannot will most likely need nursing home care. Very few families have enough people and support to care for such a patient at home.
The hospital social workers, ICU doctors and Neurosurgeons will help you with placement into an appropriate facility.
You should visit the facility yourself before agreeing to transfer. Be sure it is acceptable to you and the rest of your family.
Questions to Ask
- Will my loved one be able to care for him or herself?
- What will rehab be able to do?
- What is the likelihood of doing well enough in a nursing home to be able to get into rehab?
- What can we expect our loved one to be able to do on her or his own?
- If a tracheostomy is still in, when will it be able to come out?
When is Brain Trauma Fatal?
Some brain injuries are so severe they are instantly fatal or very soon afterwards
In the ICU, most deaths from brain trauma happen if brain pressures cannot be controlled.
The high pressures prevent blood and oxygen from getting to brain. Without blood or oxygen the brain irreversibly dies. This is brain death
The patient will still have a heart rate and blood pressure; but no brain function.
Specific tests are done and often re-done to be sure the brain death diagnosis is correct.
Often this requires special studies in the hospital x ray department.
Your family should be asked to decide if they desire organ donation.
Once every family member understands the situation and are in agreement, preparation can begin for organ transplantation
If there will not be organ donation , then all the life support is removed.
Questions to Ask
- Is there any chance of recovery from brain death?
- What if we do not agree with the brain death diagnosis, what can we do?
- Can we request another opinion or an Ethics consultation
- Can we move our loved one to another hospital?
- What happens if and when the life support is removed?
- Who will talk to us about organ donation?
- How do we decide about organ donation?
- How does organ donation work?